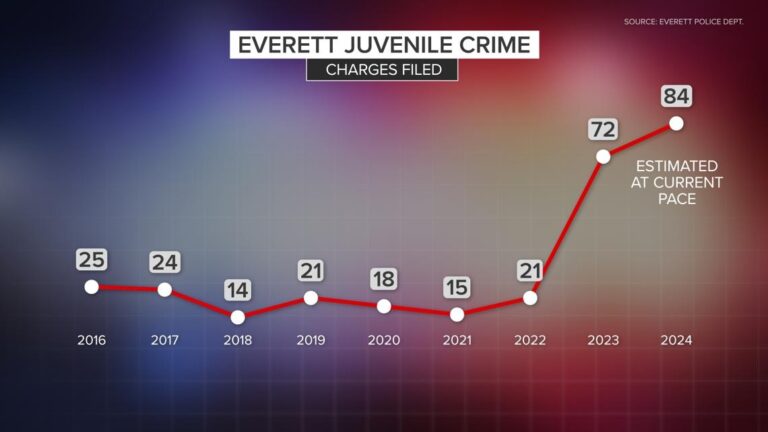
Resurgence of Juvenile Crime in Washington Post-Pandemic
Recent statistics indicate that juvenile crime rates in Washington State have rebounded to levels comparable to those seen before the COVID-19 pandemic disrupted societal norms. Law enforcement agencies report that offenses committed by minors, especially in metropolitan areas such as Seattle and Tacoma, have stabilized after fluctuating during lockdown periods. Crimes including vandalism, minor theft, and assaults have returned to figures similar to those recorded in 2019, signaling a reversion to pre-pandemic behavioral trends among youth. This resurgence underscores the ongoing need for focused community programs aimed at addressing the social and economic factors influencing juvenile delinquency.
However, vehicle thefts involving juveniles have surged dramatically, surpassing previous records and prompting heightened concern among officials and residents alike. This alarming increase has led to intensified law enforcement efforts targeting prevention and rapid recovery of stolen vehicles. Key highlights from recent reports include:
- A nearly 32% rise in vehicle thefts committed by minors compared to pre-pandemic data
- Concentration of incidents primarily in King and Pierce counties
- Most stolen vehicles are recovered within two days, though associated property damage remains costly
| Juvenile Crime Category | 2019 Monthly Average | 2023 Monthly Average | Percentage Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vandalism | 450 cases | 460 cases | +2.2% |
| Petty Theft | 380 cases | 390 cases | +2.6% |
| Assault | 150 cases | 155 cases | +3.3% |
| Vehicle Theft | 110 cases | 145 cases | +31.8% |
Alarming Increase in Juvenile Vehicle Thefts Across Washington
The state has witnessed a sharp escalation in vehicle thefts perpetrated by individuals under 18, reversing the downward trend observed during the pandemic’s peak. Authorities link this surge to a mix of factors including renewed social gatherings, economic instability, and the suspension of youth engagement programs that previously provided structure and mentorship. The repercussions extend beyond financial losses, as stolen vehicles often become involved in dangerous driving incidents, heightening public safety risks.
Primary contributors to the rise in juvenile car thefts include:
- Reduced availability of after-school and community programs
- Peer pressure and recruitment by local gangs targeting vulnerable youth
- Greater access to vehicles with minimal security features
- Economic hardships intensified by the pandemic’s lingering effects
| Age Bracket | Proportion of Vehicle Theft Arrests | Increase Since 2020 |
|---|---|---|
| Under 16 | 22% | +8% |
| 16-17 | 48% | +12% |
| 18-20 | 30% | +5% |
Understanding the Root Causes of Increasing Juvenile Offenses
Specialists in youth behavior and criminology emphasize that the rise in juvenile offenses in Washington stems from a multifaceted set of social, economic, and psychological influences. The pandemic’s disruption to education systems, extracurricular activities, and family dynamics has left many young people vulnerable. Experts also highlight the growing impact of digital media and increased screen time, which can amplify risky behaviors and exposure to negative influences.
Additional factors contributing to this trend include:
- Economic strain leading to decreased parental supervision
- Exposure to violence within communities
- Insufficient access to mental health services tailored for youth
- Involvement with peer groups engaged in unlawful activities
Law enforcement stresses the necessity of comprehensive intervention strategies that tackle these underlying issues, particularly to address the spike in vehicle thefts.
| Contributing Factor | Level of Impact | Recommended Intervention |
|---|---|---|
| Interrupted Education | High | After-school tutoring and mentorship programs |
| Limited Mental Health Resources | Moderate | Community-based counseling services |
| Family Economic Stress | High | Financial assistance and support networks |
| Peer Group Influence | High | Engagement in positive youth activities |
Strategies and Policies to Reduce Youth Involvement in Auto Theft
Community leaders and policymakers are advocating for a holistic approach to combat the surge in juvenile vehicle thefts. Proposed initiatives include expanding mentorship opportunities, increasing access to after-school programs, and boosting funding for vocational training to equip young people with practical skills and constructive outlets. Collaboration among law enforcement, educational institutions, and social service agencies is seen as vital to fostering environments that discourage criminal behavior.
Furthermore, there is a push for a balanced justice system that combines stricter legal consequences with restorative justice models tailored to juveniles. This approach aims to hold offenders accountable while promoting rehabilitation and reducing repeat offenses. Key policy recommendations include:
- Community outreach programs focused on at-risk youth
- Investment in early prevention initiatives to address root causes
- Enhanced data sharing between law enforcement and schools for timely intervention
- Active involvement of parents and guardians to reinforce positive behaviors
| Policy Area | Anticipated Benefit |
|---|---|
| Mentorship and After-School Engagement | Decrease in idle time and promotion of positive role models |
| Restorative Justice Programs | Reduction in recidivism and encouragement of responsibility |
| Improved Data Coordination | Early detection and support for vulnerable youth |
Final Thoughts on Juvenile Crime Trends in Washington
As juvenile crime rates in Washington revert to pre-pandemic norms, the significant rise in vehicle thefts by minors remains a pressing concern. Authorities continue to monitor these developments closely, emphasizing the critical role of community involvement and preventative strategies in mitigating youth crime. Ongoing coverage and analysis will provide further insights into the effectiveness of implemented measures and evolving trends in juvenile delinquency across the state.