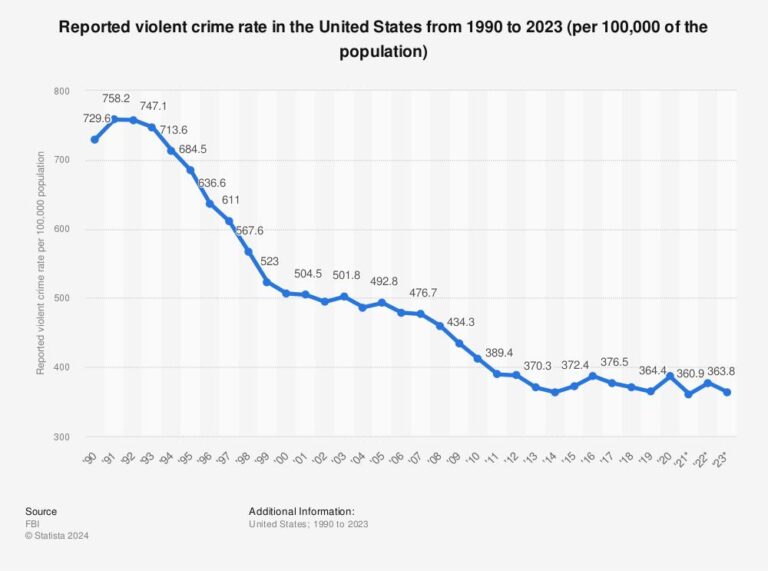
Understanding the Complex Rise in Violent Crime Across the United States
Unraveling the Multifaceted Causes Behind Increasing Violent Crime
In recent years, numerous American cities have experienced a notable escalation in violent crime rates, leaving communities and officials searching for clear answers. Experts emphasize that this surge cannot be attributed to a single cause; rather, it stems from a convergence of diverse social, economic, and systemic influences. Factors such as economic hardship, evolving law enforcement tactics, and community dynamics intertwine to create a complicated picture that defies simple explanations.
Among the primary contributors under examination are:
- Economic challenges: Rising unemployment and growing income inequality intensify social pressures and unrest.
- Policing transformations: Variations in law enforcement funding, priorities, and community engagement impact crime rates differently across regions.
- Social upheaval: The psychological toll of the COVID-19 pandemic and cultural shifts have disrupted social cohesion.
- Firearm accessibility: The widespread availability of guns remains a significant and complex factor in violent offenses.
| Factor | Effect on Crime | Strength of Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Hardship | Financial stress linked to increased violent acts | Moderate |
| Policing Changes | Shifts in enforcement correlate with crime rate fluctuations | Developing |
| Social Disruption | Pandemic-related isolation possibly fueling violence | Speculative |
| Gun Availability | Easy access facilitating violent incidents | Strong |
Socioeconomic and Policy Influences Shaping Crime Patterns
The evolving landscape of violent crime is deeply influenced by broader societal shifts and legislative reforms. Persistent economic inequality, systemic disinvestment in marginalized communities, and ongoing social injustices continue to exacerbate tensions. Meanwhile, criminal justice reformsŌĆösuch as efforts to reduce incarceration rates and modify sentencing guidelinesŌĆöhave introduced new dynamics that affect public safety in complex ways.
Critical societal and policy factors include:
- Public health emergencies: The COVID-19 crisis intensified social isolation and disrupted traditional crime prevention efforts.
- Legislative reforms: Decarceration policies have decreased prison populations but may have shifted some challenges into communities.
- Resource limitations: Cuts to social services have reduced funding for youth programs and crisis intervention teams.
- Law enforcement evolution: New policing models and accountability measures continue to influence crime deterrence and reporting.
| Factor | Impact | Timeframe |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Inequality | Heightened social frustration and instability | Long-term |
| Pandemic Aftereffects | Increased social isolation and stress | Short to medium-term |
| Criminal Justice Reforms | Changes in incarceration impacting community safety | Ongoing |
| Cuts to Social Services | Reduced preventative outreach and support | Medium-term |
Local Variations and Community Responses to Crime
The impact of violent crime varies widely across different communities, reflecting unique local conditions and responses. While some urban areas face escalating gun violence that strains law enforcement and erodes public trust, others struggle with persistent poverty, limited educational opportunities, and social fragmentation. These disparities highlight the necessity of tailored approaches that address the specific historical, economic, and social contexts of each community.
Local factors influencing crime trends include:
- Economic downturns causing job losses and increased poverty rates
- Diverse policing tactics and community engagement levels
- Changes in illicit drug markets and substance abuse trends
- Variations in local governance and availability of social support services
| City | Dominant Crime Driver | Community Initiatives |
|---|---|---|
| Metroville | Economic Hardship | Vocational training and employment programs |
| Riverside | Drug-related violence | Enhanced police patrols and drug intervention teams |
| Eastwood | Community Fragmentation | Neighborhood outreach and youth mentorship |
Comprehensive Approaches to Mitigate Violent Crime
Addressing the rise in violent crime requires a holistic strategy that acknowledges the intricate web of underlying causes. Effective solutions must go beyond punitive measures to tackle the root social, economic, and psychological factors that foster violence. Collaboration between policymakers, law enforcement, and community organizations is essential to implement programs that enhance education, mental health support, and economic opportunities, while reforming justice systems to prioritize rehabilitation.
Core components of a multifaceted crime reduction strategy include:
- Strengthening Community Relations: Enhancing trust and cooperation between residents and police to enable proactive crime prevention.
- Economic Empowerment: Combating poverty and unemployment to reduce conditions that often lead to criminal activity.
- Expanding Mental Health Services: Providing accessible counseling and treatment to address trauma-related violence.
- Investing in Youth Programs: Offering educational and recreational opportunities to divert young people from criminal pathways.
| Initiative | Anticipated Outcome |
|---|---|
| Workforce Development Programs | Reduce repeat offenses by providing sustainable employment |
| Community-Oriented Policing | Build mutual trust and lower conflict incidents |
| Mental Health Outreach | Decrease violence linked to untreated mental health issues |
| After-School and Mentorship Programs | Engage youth positively and prevent criminal involvement |
Final Thoughts: Navigating the Path Forward
The persistent increase in violent crime across the United States presents a complex challenge that resists simple solutions. Economic inequality, social disruption, and evolving law enforcement practices all contribute to this multifaceted issue. Moving ahead, it is imperative to foster comprehensive research and open dialogue that inform nuanced policies and community-driven initiatives. Only through coordinated, evidence-based efforts can we hope to reduce violence and promote safer, more resilient communities nationwide.