Understanding the Current Debt Ceiling Crisis: Economic Risks and Political Dynamics
Economic Risks and Market Reactions Amid the Debt Ceiling Deadlock
The persistent deadlock in Washington over raising the debt ceiling is casting uncertainty over the U.S. economy, unsettling investors and financial markets alike. If lawmakers fail to agree on increasing the borrowing limit, the government risks halting payments on its obligations, which economists warn could lead to a spike in borrowing costs, a potential downgrade of the U.S. credit rating, and widespread market turbulence. This uncertainty is already contributing to heightened volatility in stock and bond markets, as investors brace for possible disruptions.
Primary Economic Concerns Include:
- Risk of Government Shutdown: Without an increased debt ceiling, federal operations and services may face interruptions, affecting millions of Americans.
- Slowed Economic Momentum: Market instability could reduce consumer confidence and business investments, potentially hindering economic recovery efforts.
- International Financial Impact: Given the U.S. dollar’s role as the world’s reserve currency, any disruption could reverberate through global markets.
- Heightened Political Uncertainty: Prolonged disputes over the debt ceiling raise questions about the government’s ability to manage fiscal policy effectively.
| Impact Category | Immediate Effects | Long-Term Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rates | Noticeable increase | Elevated baseline rates |
| Market Stability | Sharp fluctuations | Persistent volatility |
| Creditworthiness | Agency reviews initiated | Potential downgrade |
Political Stakeholders and Their Objectives in the Debt Ceiling Negotiations
The ongoing debt ceiling debate centers on influential political figures whose decisions will shape the nation’s fiscal future. Congressional leaders from both parties wield significant influence: Republicans typically advocate for spending reductions and fiscal discipline, while Democrats prioritize safeguarding social welfare programs and minimizing cuts that could affect vulnerable groups. The White House, under the President’s leadership, aims to uphold the country’s credit integrity while advancing its broader economic policies. Crucial legislative bodies, including the House Ways and Means Committee and the Senate Budget Committee, are instrumental in formulating potential compromises to resolve the stalemate.
The stakes are immense, with each faction balancing political capital, public opinion, and economic ramifications. Below is an overview of the main actors and their respective goals and risks:
| Political Entity | Primary Objective | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| House Republicans | Implement spending cuts and fiscal reforms | Risk of government shutdown and voter dissatisfaction |
| Senate Democrats | Protect social programs and avoid deep cuts | Criticism for fiscal irresponsibility |
| The Executive Branch | Maintain creditworthiness and economic stability | Political backlash and policy setbacks |
| Congressional Committees | Develop viable legislative solutions | Potential gridlock and diminished influence |
Lessons from History: Recurring Patterns in Debt Ceiling Crises
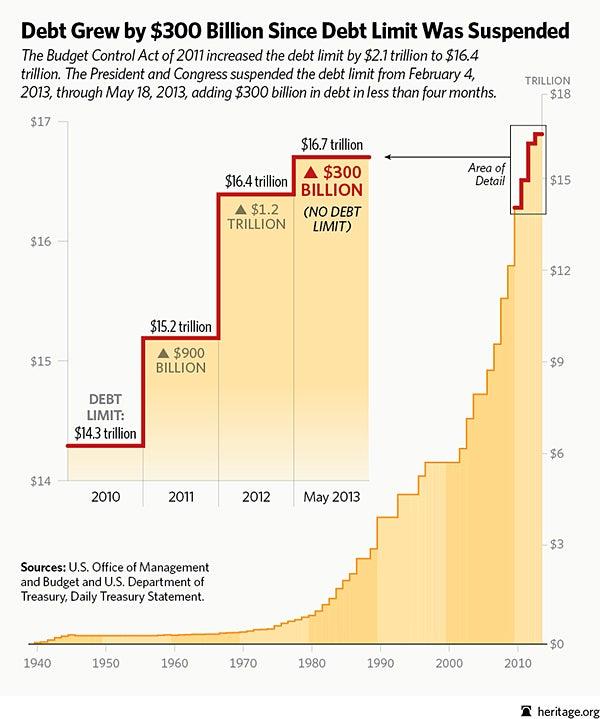
The United States has faced numerous debt ceiling confrontations over the past several decades, each revealing recurring themes in the nation’s fiscal and political environment. These standoffs often reflect deeper ideological conflicts over government spending priorities rather than immediate financial necessity. Recognizing this historical context helps clarify that debt ceiling crises frequently serve as strategic leverage points in broader budget negotiations.
Historical Factors Influencing Debt Ceiling Disputes:
- Use of the debt limit as a political bargaining tool.
- Significant effects on global financial markets and credit ratings.
- Alignment of deadlines with election cycles and legislative sessions.
- Shifting public attitudes oscillating between alarm and complacency.
| Year | Result | Duration (Days) |
|---|---|---|
| 1995-1996 | Extended Government Shutdown | 21 |
| 2011 | First U.S. Credit Rating Downgrade | 37 |
| 2013 | Brief Government Shutdown | 16 |
| 2021 | Last-Minute Debt Ceiling Suspension | 5 |
Proactive Measures to Prevent Future Debt Ceiling Crises
To break the cycle of recurring fiscal impasses, Congress could adopt several reforms aimed at enhancing long-term financial stability. One promising solution is to automate adjustments to the debt ceiling based on projected government spending and revenue, thereby minimizing political standoffs. Another approach involves implementing multi-year or biennial budgeting, which would provide lawmakers with a longer-term fiscal outlook and reduce last-minute budgetary pressures.
Additionally, establishing a formal process that links increases in the debt limit directly to approved appropriations could prevent the government from defaulting due to political deadlock. Complementary reforms might include greater transparency in debt negotiations and the creation of bipartisan committees dedicated to managing debt ceiling discussions well before deadlines. The table below summarizes potential reforms and their anticipated benefits:
| Reform Initiative | Objective | Expected Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Automated Debt Ceiling Adjustments | Synchronize debt limit with fiscal forecasts | Reduce political brinkmanship |
| Biennial Budgeting | Extend fiscal planning horizon | Enhance budget predictability |
| Debt Limit Tied to Appropriations | Ensure debt ceiling matches spending | Mitigate default risk |
| Bipartisan Oversight Committees | Specialized management of debt negotiations | Facilitate early conflict resolution |
Conclusion: Navigating the Debt Ceiling Challenge
As the debate over the debt ceiling intensifies once again, the implications for the U.S. economy and political landscape remain profound. A clear grasp of the economic risks, political dynamics, historical context, and potential reforms is essential for understanding this complex issue. Vigilant coverage and informed public discourse will be critical as policymakers work to resolve this recurring fiscal challenge and safeguard the nation’s financial future.