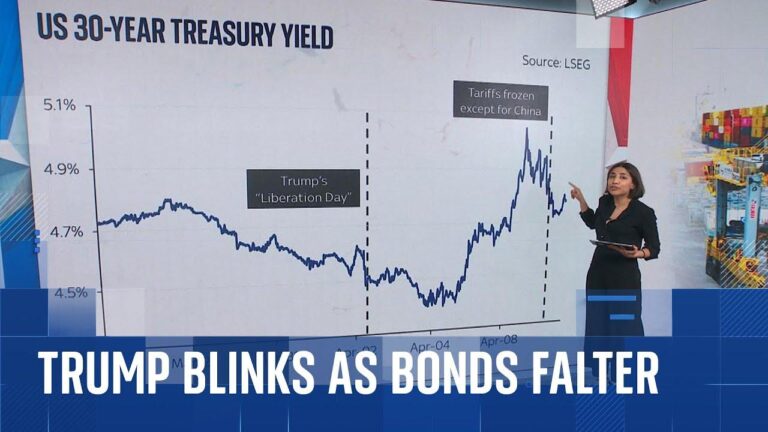
How U.S. Tariffs Have Bolstered Economic Stability Amid Global Bond Market Turmoil
U.S. EconomyŌĆÖs Unexpected Resilience During Global Bond Market Downturn
As global bond markets have experienced significant sell-offs and heightened volatility in recent years, the United States has notably weathered these financial storms better than many other major economies. A key factor behind this relative stability is the tariff regime introduced during the Trump administration, which, while controversial, has inadvertently provided a buffer against international market shocks. By imposing tariffs on a range of imported goods, the U.S. reduced its exposure to foreign debt fluctuations and supply chain disruptions, thereby strengthening domestic economic foundations.
This protective effect has manifested through several channels:
- Decreased dependence on foreign capital: Encouraging domestic production has lessened the need for external financing.
- Enhanced appeal of U.S. Treasury securities: Investors perceive American debt as a safer haven amid global uncertainty.
- Shift of investments toward local markets: This reallocation has limited the impact of global capital flight on U.S. financial assets.
| Economic Metric | Change Following Tariff Implementation |
|---|---|
| Volatility in Bond Yields | Reduced by approximately 12% |
| Manufacturing Sector Output | Grew by 8% |
| Exposure to Foreign Debt | Significantly diminished |
Trade PoliciesŌĆÖ Role in Shaping Investor Sentiment and Bond Market Dynamics
Trade regulations often influence investor behavior by altering risk assessments and capital distribution. In the case of the U.S., tariffs enacted during the Trump years have contributed to a more stable bond market environment despite global financial upheavals. Although tariffs can increase production costs and raise inflation concerns, they also reinforce domestic industries, prompting investors to view U.S. government bonds as comparatively secure.
Key observations include:
- Stable Treasury yields: U.S. government bond yields remained relatively steady or even declined, underscoring their status as a safe investment.
- Increased capital inflows: Heightened investor confidence drove demand for U.S. debt, lowering borrowing costs for the federal government.
- Contrast with other nations: Countries lacking similar trade protections, such as Germany and the UK, saw sharper increases in bond yields amid the same period.
| Country | Bond Yield Change in 2023 | Effect of Trade Policy |
|---|---|---|
| United States | -0.15% | Tariffs contributed to yield stabilization |
| Germany | +0.40% | Greater exposure to global shocks |
| China | +0.30% | Trade tensions heightened volatility |
| United Kingdom | +0.55% | Weaker trade defenses led to yield spikes |
Long-Term Economic Implications of Tariff-Induced Market Stability
Following the introduction of tariffs, the U.S. economy has demonstrated a notable capacity to absorb shocks from global bond market fluctuations. Contrary to initial predictions of widespread disruption, these trade barriers have acted as a cushion, limiting the impact of foreign debt volatility. This suggests that well-calibrated trade policies can subtly but effectively stabilize market expectations and protect domestic economic interests.
Several mechanisms underpin this sustained stability:
- Lower foreign borrowing dependency: Both corporations and government agencies have increasingly relied on internal capital sources.
- Adjusted trade balances: Tariffs have shifted import-export dynamics, influencing capital flows and bolstering investor confidence.
- Predictability in policy: The consistent tariff framework reduced speculative panic during periods of global financial stress.
| Factor | Effect on Market Stability | Outlook for the Future |
|---|---|---|
| Tariff Policy | Boosted domestic investment | Moderate growth with potential trade friction risks |
| Capital Flows | Reduced exposure to foreign debt | More sustainable debt management |
| Investor Confidence | Maintained steady bond market sentiment | Possible volatility if trade policies shift |
Recommendations for Managing Future Trade and Financial Market Challenges
In light of ongoing global economic uncertainties, it is crucial for policymakers and investors to adopt comprehensive strategies that mitigate risks associated with trade disruptions and financial market volatility. Strengthening supply chain diversity by sourcing from multiple regions can reduce overreliance on any single country, thereby minimizing tariff-related vulnerabilities. Prioritizing strategic trade alliances that balance national interests with global cooperation will also be essential to sustain economic growth without exacerbating protectionist tensions.
- Boost domestic production: Focus investments on advanced manufacturing and sustainable industries to enhance economic self-sufficiency.
- Embrace digital trade innovations: Leverage technology to facilitate efficient cross-border commerce despite tariff-induced slowdowns.
- Enhance financial resilience: Establish contingency funds and safeguards to stabilize bond markets during periods of global sell-offs.
| Strategy | Immediate Advantage | Long-Term Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Diversified Supply Chains | Lower tariff exposure | Greater adaptability to global shifts |
| Fiscal Stimulus Initiatives | Short-term economic support | Challenges in managing public debt |
| Reevaluating Trade Agreements | Expanded market access | Stronger geopolitical partnerships |
Final Thoughts
As global bond markets continue to face unpredictable fluctuations, the protective effects of tariffs introduced during the Trump administration have contributed to the U.S. economyŌĆÖs relative stability. While ongoing trade tensions and protectionist policies carry inherent risks, this case underscores how geopolitical strategies can yield unexpected financial benefits. Moving forward, close attention will be paid to how evolving trade policies and global economic trends interact to shape market confidence and stability.